Panama City Physicians: The Signs, Causes, and Treatment of Gallstones
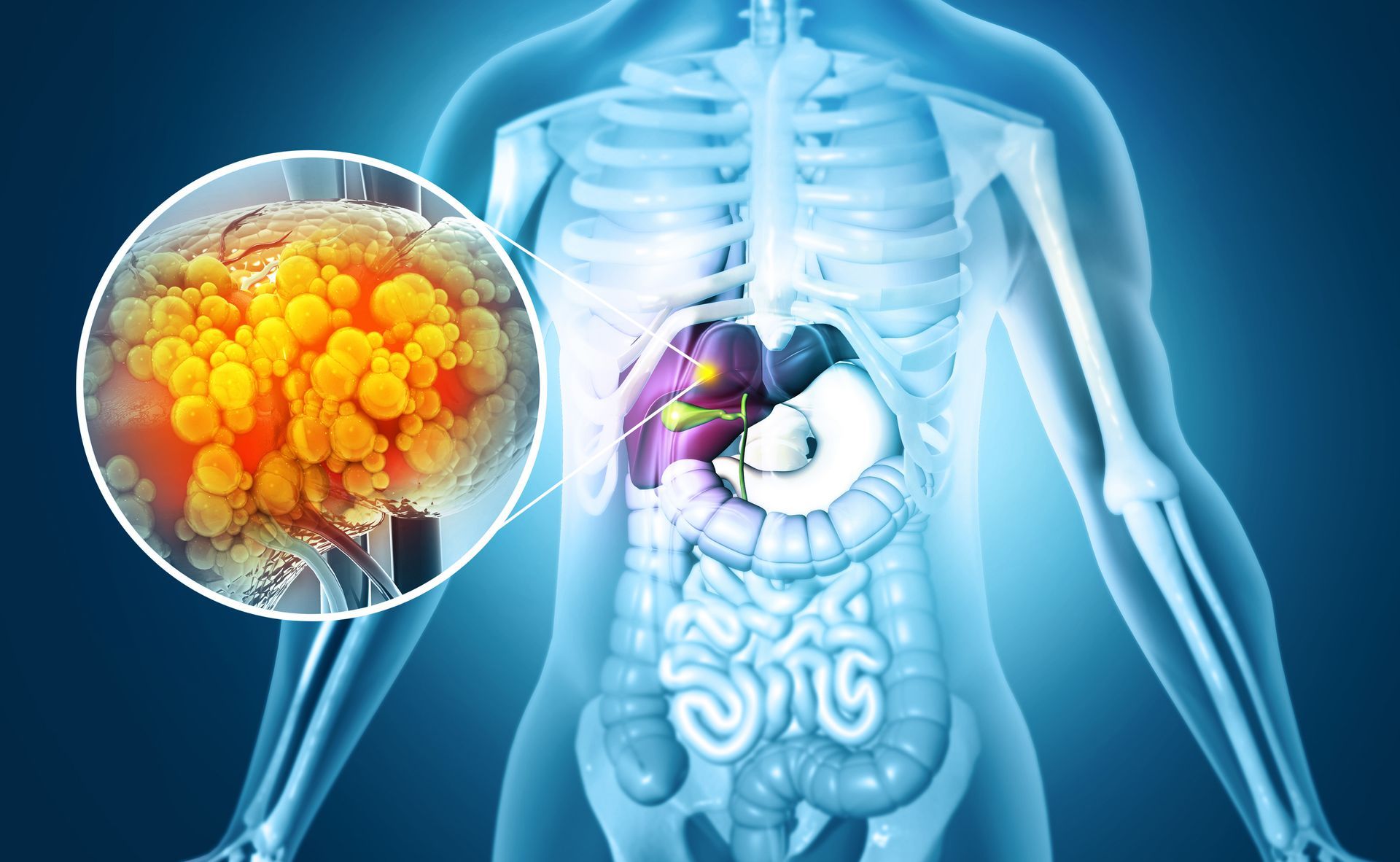
The gallbladder is a small organ under the liver that stores bile and helps aid in digestion. During the digestive process, the gallbladder releases bile into the small intestines to help break down fats. The most common gallbladder complications are the occurrence of gallstones.
What are Gallstones?
Gallstones are actually not stones at all. They are hardened pieces of digestive fluid that can range in size from a grain of rice up to a golf ball-sized mass. Many people will develop gallstones and not even know it. Pain and symptoms generally only occur when gallstones become lodged in the bile ducts.
What Causes Gallstones?
The majority of gallstones are made of cholesterol and occur when bile cannot break down all the cholesterol in the gallbladder. Though less common, gallstones can also be made of bilirubin. This happens when there is an excess of bilirubin produced by the liver to break down old red blood cells. Certain conditions, such as damage to the liver and blood disorders, can cause the liver to produce more bilirubin than normal. When the bile cannot break down all the bilirubin, they can become gallstones. Gallstones can also be caused by a lazy gallbladder. If the gallbladder does not fully empty itself, the bile becomes concentrated and causes stones to form.
What are the Symptoms of Gallstones?
Many gallstones do not present any signs of their presence. For those that do, there are several associated symptoms:
- Pain in your upper right or middle abdomen
- Pain in your right shoulder
- Stomach pain
- Nausea and vomiting
- Jaundice
- Indigestion and diarrhea
- Dark urine
- Light-colored stool
How Are Gallstones Diagnosed?
If you’re experiencing symptoms of gallstones, your doctor will likely begin with a physical examination. Other diagnostic methods may include:
- Blood tests: Your doctor may order a blood test to check for other issues and also measure the amount of bilirubin in your blood.
- Ultrasound: An ultrasound transmits high-frequency soundwaves into the body that create an accurate picture of your organs, including the gallbladder.
- Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP): This method can work as both a diagnosis and treatment. Your doctor will insert a small, flexible tube with an attached camera into your mouth and run it down to your small intestines. A dye is injected to make the gallstones visible. If the stones are in the bile duct, this device can then remove the stones from the duct.
- Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography: Similar to how an ultrasound uses soundwaves, this procedure magnetic fields and radio waves to create images of your internal organs.
How Are Gallstones Treated?
If you have asymptomatic gallstones, or “silent gallstones,” they do not need to be treated. Symptomatic gallstones may be treated with medications that are formulated to dissolve gallstones. Under most circumstances, gallbladder removal surgery called a cholecystectomy is performed. Having your gallbladder removed does not affect your body's digestive process, and a person can live their everyday life after surgery. The most common side effect of gallbladder removal is a temporary increase in diarrhea.
Who is at Risk for Gallstones?
There are several risk factors involved with gallstones. You may find yourself at higher risk if you:
- Are female
- Are pregnant
- Are over the age of 40
- Experience rapid weight loss
- Have diabetes
- Have Crohn’s disease
- Eat a high fat or high cholesterol diet
- Are obese
- Live a sedentary lifestyle
- Have a family history of gallstones
If you are experiencing symptoms of gallstones, schedule an appointment with our team of trusted gastroenterologists today. Our doctors can help diagnose and treat your gallstones so you can get back to the life you love.
CONTACT
850-763-5409
ADDRESSES
4 LOCATIONS
204 E 19th Street, B, Panama City
12216 Panama City Beach Pkwy, D, Panama City Beach
4295 3rd Ave, Marianna
101 Good Morning St., 109B, Port St. Joe
Subscribe to our newsletter:
subscribe to our newsletter
We will get back to you as soon as possible.
Please try again later.