Colorectal Cancer Symptoms, Screening, and Treatment
Colon cancer is the second leading cause of death for men and women in the United States of America. This is a disease that can be successfully identified and treated, however, screening is essential. This begs the questions of “what is colorectal cancer?”, “what are the symptoms?”, “how do you get screened?”, and “how is it treated?”.
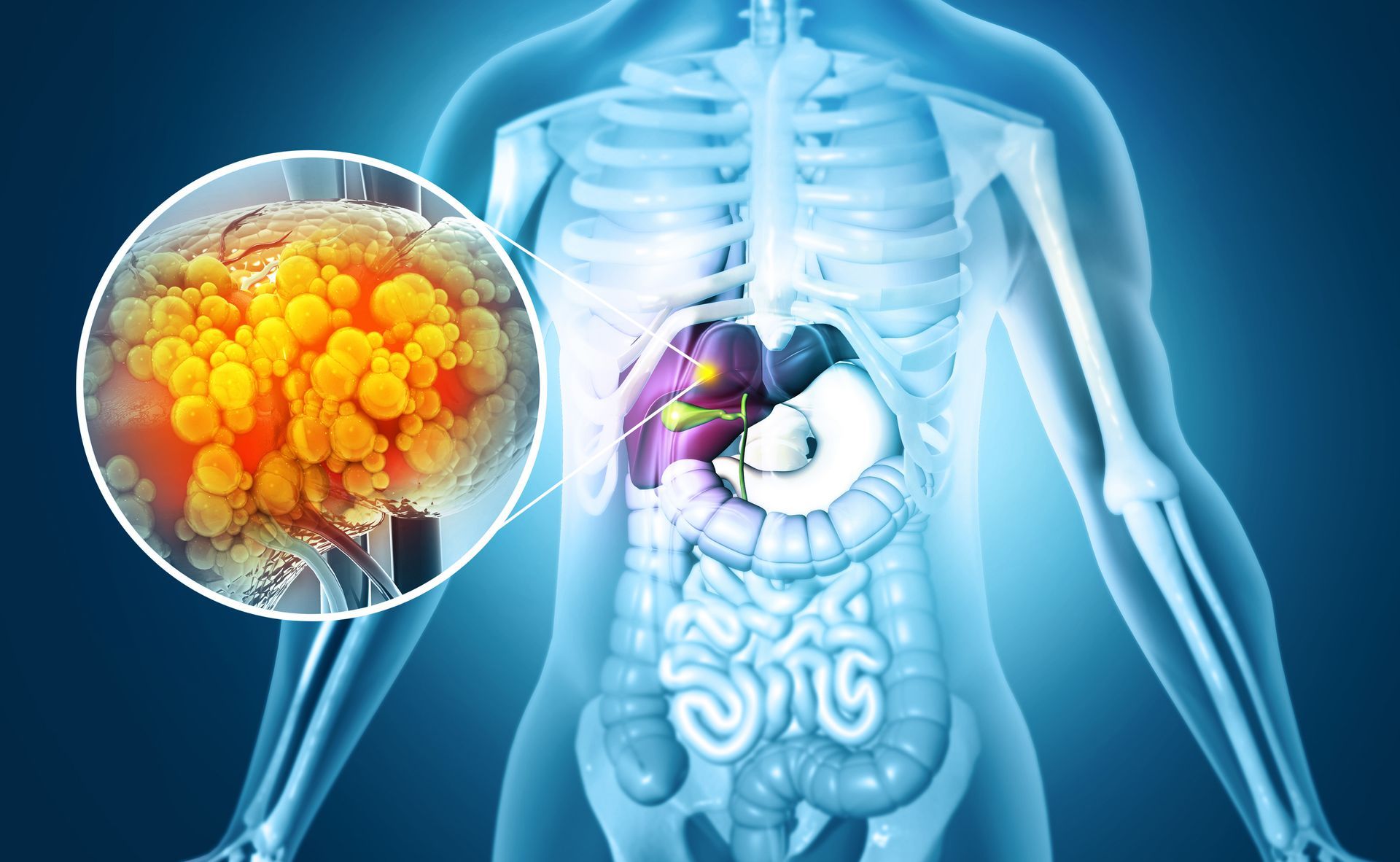
What is Colon Cancer?
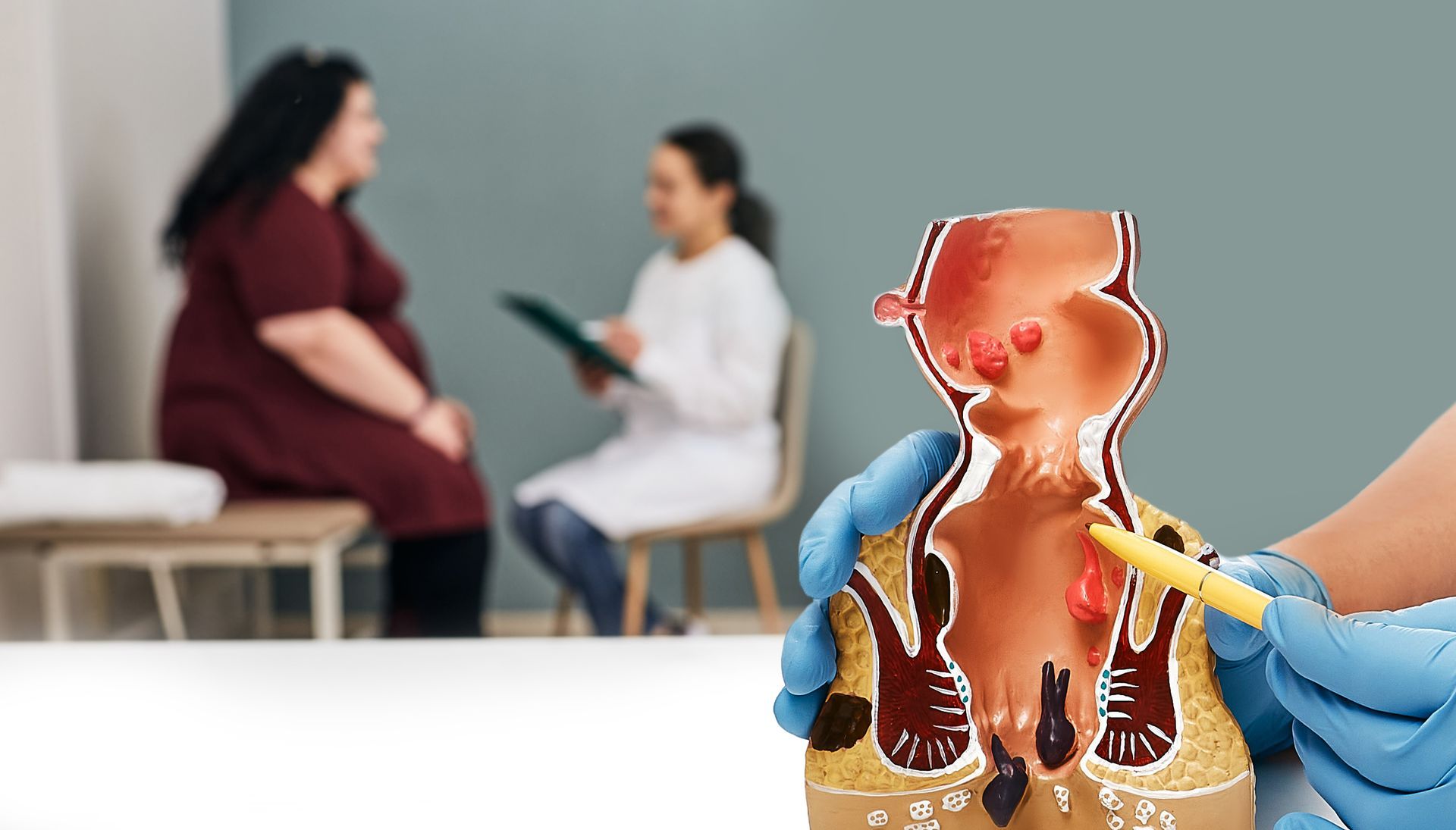
Colorectal cancer develops in the colon or rectum of your digestive system. It typically occurs as a precancerous growth that is referred to as a polyp. Polyps grow on the inner lining of the colon or rectum, and can eventually develop into a malignant growth. Lifestyle factors like smoking, excessive drinking, obesity, as well as heredity are all risk factors for colorectal cancer.
What are the Symptoms of Colorectal Cancer?
Colon cancer symptoms can mirror the symptoms of other GI conditions like IBS (irritable bowel syndrome), inflammatory bowel disease, or hemorrhoids. If you experience a change in bowel habits, unexpected weight loss, rectal bleeding, persistent abdominal pain, blood stool, or prolonged cramping, you should consult a gastroenterologist.
What is Colon Cancer Screening?
Colorectal cancer screening can reduce you chance of dying by 60%. An annual colonoscopy, if you are over 45 years old or earlier if you are at high risk, can make a tremendous difference in identifying polyps or cancerous growths. Even if there are no symptoms present, you still attend an annual screening. Typically symptoms don’t occur until polyps or cancer are beyond the early stages of treatment.
How is Colon Cancer Treated?
If you have been diagnosed with colorectal cancer, there is a variety of treatment options.
- Local Treatments – The tumor can treated without affecting the entire body. This is the ideal treatment for early stage and smaller cancers.
- Systematic Treatments – Drugs can be used to treat colorectal cancer as they reach the cancer cells throughout the body. This includes chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy.
- Gastroenterologist – This specialist treats GI and digestive disorders.
- Surgical Oncologist – This specialist uses surgery to treat cancer.
- Colorectal Surgeon – This surgeon uses surgery to treat colon and rectum diseases.
- Medial Oncologist – This specialist treats cancer with radiation therapy.
- Radiation Oncologist - This specialist uses chemo and targeted therapy to treat cancer.
If you have experienced any of these symptoms, have not been screened, or have a family history of colorectal cancer, the expert, experienced staff at Digestive Diseases Center is here to help.
CONTACT
850-763-5409
ADDRESSES
4 LOCATIONS
204 E 19th Street, B, Panama City
12216 Panama City Beach Pkwy, D, Panama City Beach
4295 3rd Ave, Marianna
101 Good Morning St., 109B, Port St. Joe
Subscribe to our newsletter:
subscribe to our newsletter
We will get back to you as soon as possible.
Please try again later.