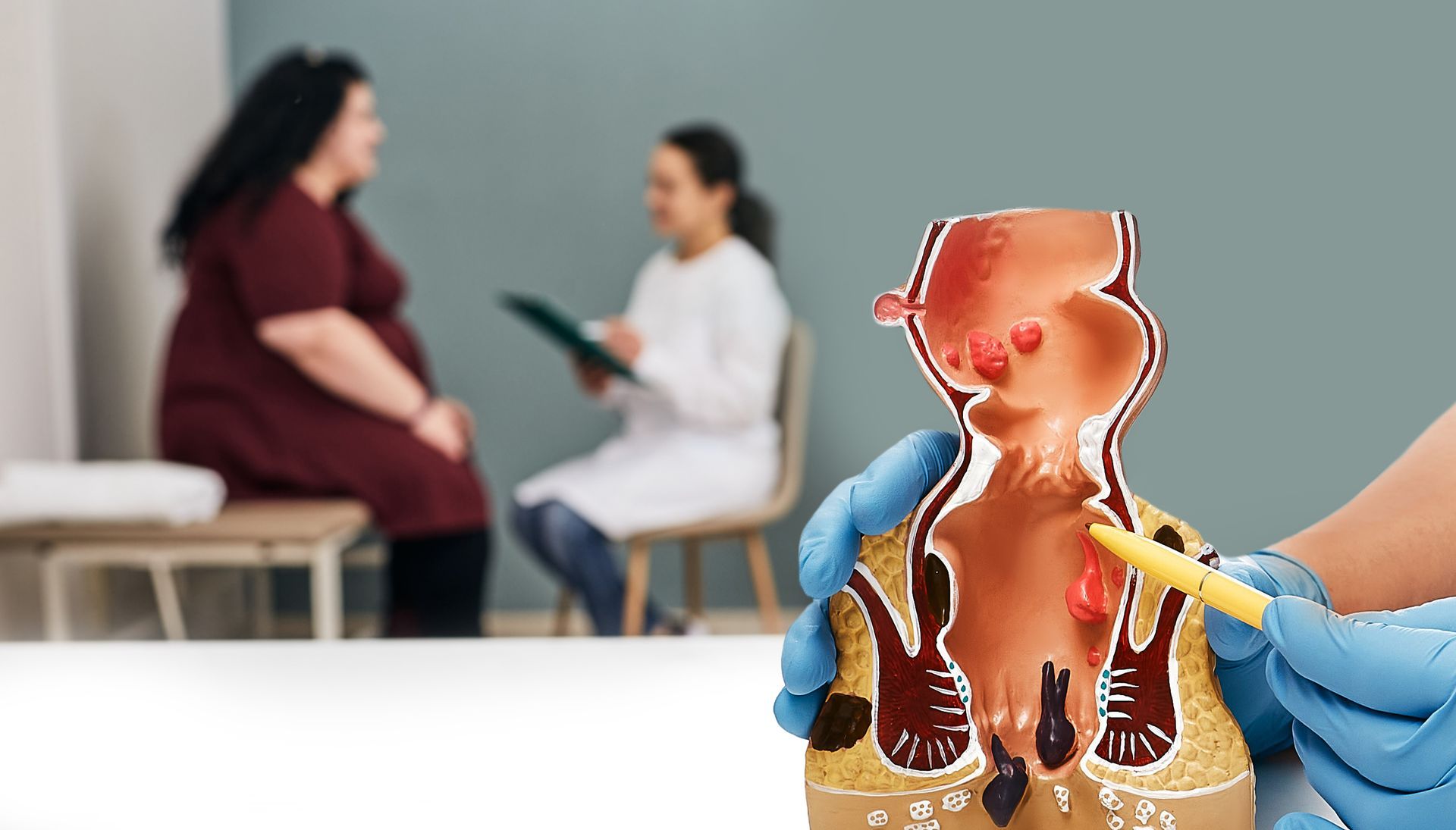
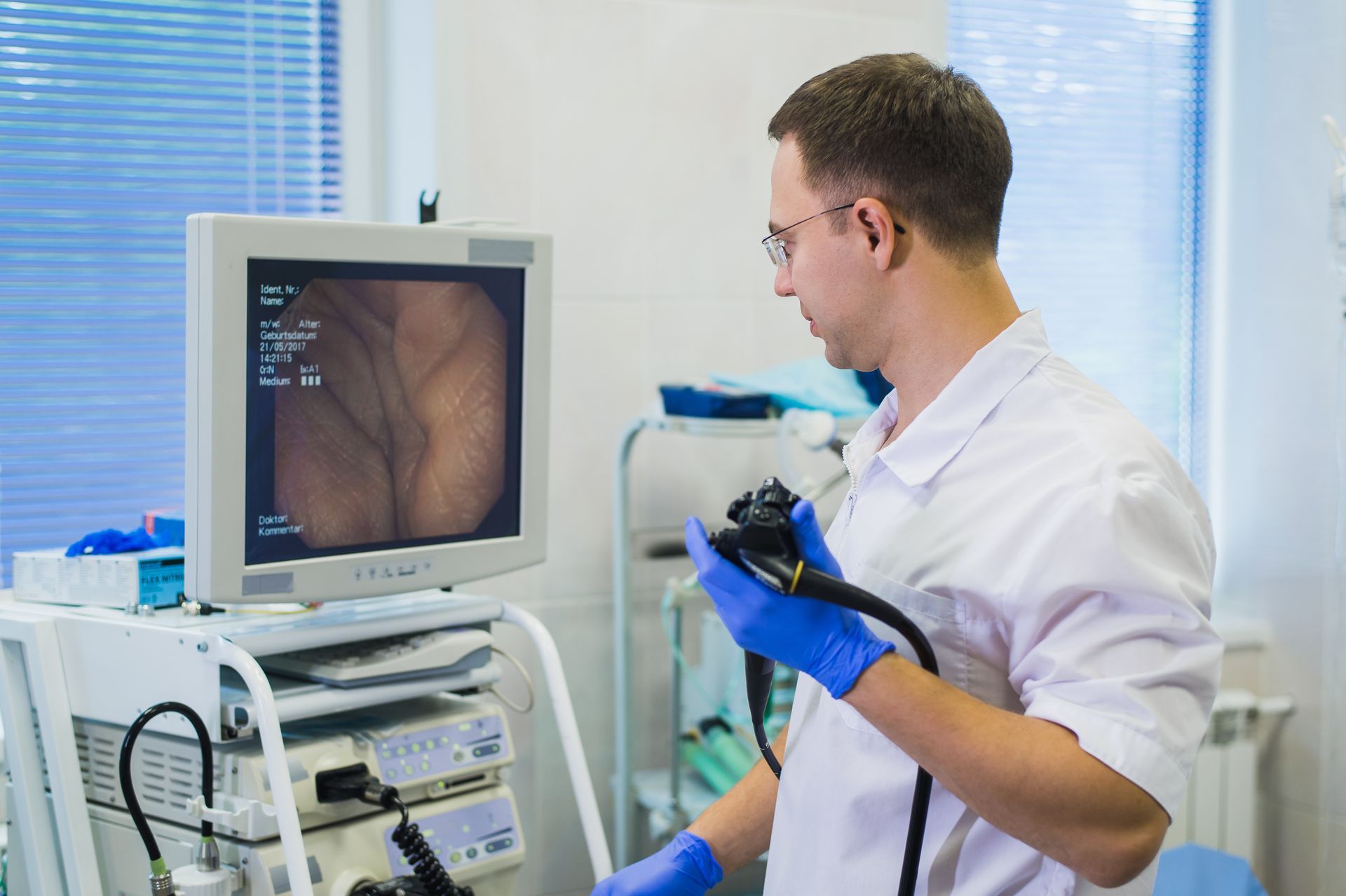
ESOPHAGEAL CANCER IN NORTHWEST FLORIDA
Your esophagus is the hollow, long tube that connects your mouth and throat to your stomach. It’s designed to move the food that you chew and swallow toward your stomach. The sixth most common cause of death in the world is esophageal cancer, which typically beings in the cells that line the inner walls of the esophagus; however, it can develop anywhere along or within the esophagus. Incidence rates vary geographically, but men tend to be more prone to developing esophageal cancer. Let’s take a closer look at the risk factors, causes, signs, and treatment options of esophageal cancer.
HAVE QUESTIONS ABOUT ESOPHAGEAL CANCER?
-
What is Esophageal Cancer?
When the cells in the esophagus experience mutation in their DNA, it causes them to uncontrollably divide and grow. As these abnormal cells accumulate, tumors can develop in the esophagus. Not only can this encroach on other parts of the body, but it can spread to other systems.
-
What are the Risk Factors for Developing Esophageal Cancer?
While the exact cause of esophageal cancer is unknown, there are several risk factors and lifestyle choices that can increase the risk of its development. The risk factors that enhance your risk of developing esophageal cancer include:
- Alcohol abuse
- Smoking
- Bile reflux
- GERD (gastroesophageal reflux disease)
- Obesity
- Achalasia (difficulty swallowing due to an unrelaxed esophageal sphincter)
-
What are the Different Types of Esophageal Cancer?
Esophageal cancer is identified by the type of cells that are mutating, and classified accordingly. Based on this classification, a treatment plan can be designed. Adenocarcinoma is one main type of esophageal cancer. This type of cancer develops in the cells of mucus-secreting glands in the esophagus, and most commonly occurs in its lower portion. This is the most common type of esophageal cancer in the U.S. and primarily affects Caucasian men.
Squamous cell carcinoma is identified by thin, flat cells along the surface of the esophagus. This type of cells are commonly found in the upper and middle sections of the esophagus. Worldwide, this is the most common type of esophageal cancer.
Small cell carcinoma, melanoma, choriocarcinoma, sarcoma, and lymphoma are other possible, although rarer types of esophageal cancer.
-
What are the Symptoms of Esophageal Cancer?
There are several distinct signs of esophageal cancer, however, the early stages of this disease typically presents no symptoms. Chest pain, pressure, and burning, along with unintended weight loss, and dysphagia (difficulty swallowing) can all indicate potential esophageal issues. Increased heartburn or indigestion, as well as unexplained hoarseness and coughing can also point toward esophageal cancer.
If you’ve experienced persistent symptoms or have received a diagnosis for Barrett’s esophagus, you need to see a doctor. An esophageal cancer screening is recommended for those with Barrett’s esophagus, and your doctor can recommend what symptoms to notice that signify the worsening of your condition.
-
What Complications can Occur with Esophageal Cancer?
There are several complications that can arise from an esophageal cancer diagnosis. Advanced esophageal cancer can become painful. Bleeding is not uncommon and is typically gradual, but can become severe and sudden at times. Obstructions within the esophagus caused by esophageal cancer can make swallowing food and liquid difficult.
-
How is Esophageal Cancer Treated?
The most common method of treatment for esophageal cancer in adults is surgery. With an operation known as esophagectomy, part of the esophagus may be removed. With the cancerous portion of the esophagus removed, the healthy part of the esophagus will be attached to the stomach. This is done by using a plastic tube or a part of the intestine.
If a tumor has caused a blockage in the esophagus, a metal stent can be placed to keep it open. Your body’s lymph nodes that are near the esophagus can also be removed and tested to determine if they contain cancerous cells.
Radiation, chemo, and laser therapy can also be utilized depending on the type, stage, and severity of the cancer.
-
How can Esophageal Cancer be Prevented?
Esophageal cancer can be prevented, or the risk reduced, by making some certain lifestyle changes. Consume alcohol moderately, if at all. Ending all tobacco use can also be helpful and healthy. Adding fruits and vegetables to your diet can create several health benefits. You should also strive to maintain a healthy weight. If you are overweight, strive or a steady and slow pace of losing one to two pounds per week, until you reach your target.
READY TO SCHEDULE AN APPOINTMENT?
GASTROENTEROLOGY BLOG
CONTACT
850-763-5409
ADDRESSES
4 LOCATIONS
204 E 19th Street, B, Panama City
12216 Panama City Beach Pkwy, D, Panama City Beach
4295 3rd Ave, Marianna
101 Good Morning St., 109B, Port St. Joe
Subscribe to our newsletter:
subscribe to our newsletter
We will get back to you as soon as possible.
Please try again later.